Geothermal energy is broadly referred to as energy that is present within the Earth that can be utilized using the available means. As shown in the figure below 46% of energy from the Sun is absorbed by the Earth. Earth has a capacity to store and release heat and act as a massive seasonal thermal storage. Geothermal energy is utilized in two broad categories. Approximately 4-6 meters below of the Earth’s surface and upto 100 meters the temperatures remain constant, equal to the locations mean annual average temperature and there of increases by 2 °C every 100 meters. Exchanging the heat with this portion of earth is one way of using geothermal energy. Besides, there are also advanced geothermal technologies that could exploit hot rock or off-shore hydrothermal, magma, gysers and geo- pressured resources. However, the former technology suits applications such as GSHP where as the latter technology suits applications such as power generation and district heat systems such as CHCP. The focus is on the former technologiy which can be easily integrated with Heat pumps to use in residential and small scale commercial applications.
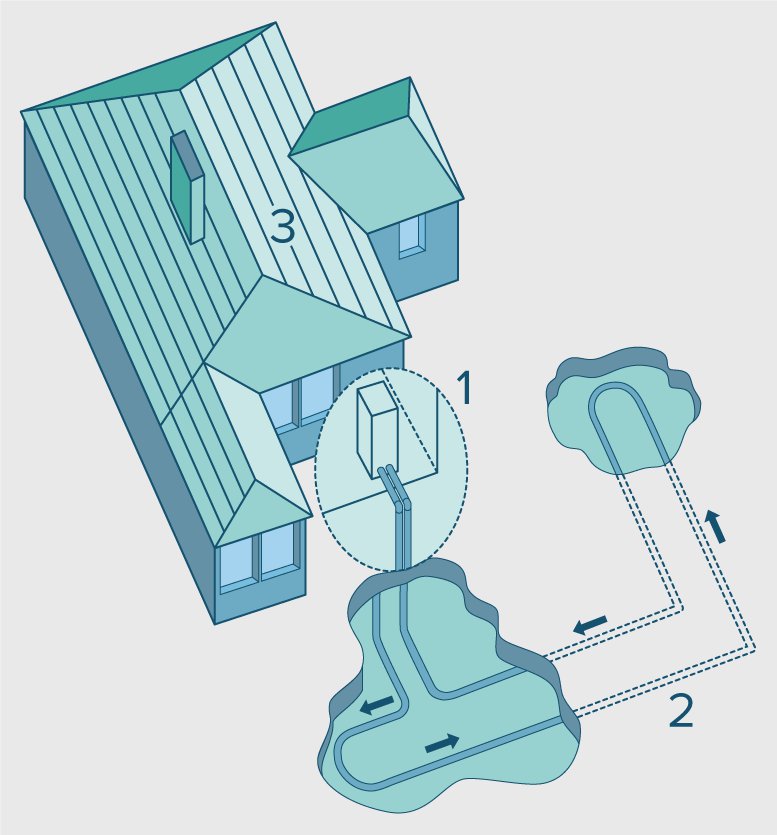
1. Heat pump
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a heat source to a heat sink against a temperature gradient. Typical heat pumps associated with GSHP are “water-to-air” systems. Heat pump operates through a DX vapour compression cycle similar to that of a room AC except that it is a reversible unit capable of reversing the cycle across the loop and thus providing both cooling and heating in different seasons using the same machine. The energy saving aspect in GSHP is that the condenser is replaced by the Earth heat exchange loop instead of the condenser exchanging the heat with the ambient air. Since the Earth heat exchange loop consists of water at a more moderate temperature than the ambient air the load on the compressor is significantly reduced thus operating the system much more efficiently than otherwise.
2. Ground source heat exchange loop
Ground source heat exchange loop is the significant aspect of a GSHP system. The heat is exchanged between the heat pump and the ground through this loop. This happens by two methods; open loop and closed loop. Typically water is circulated through this loop using a pump which acts as a medium of heat exchange.
| Open loop | Closed loop |
|---|---|
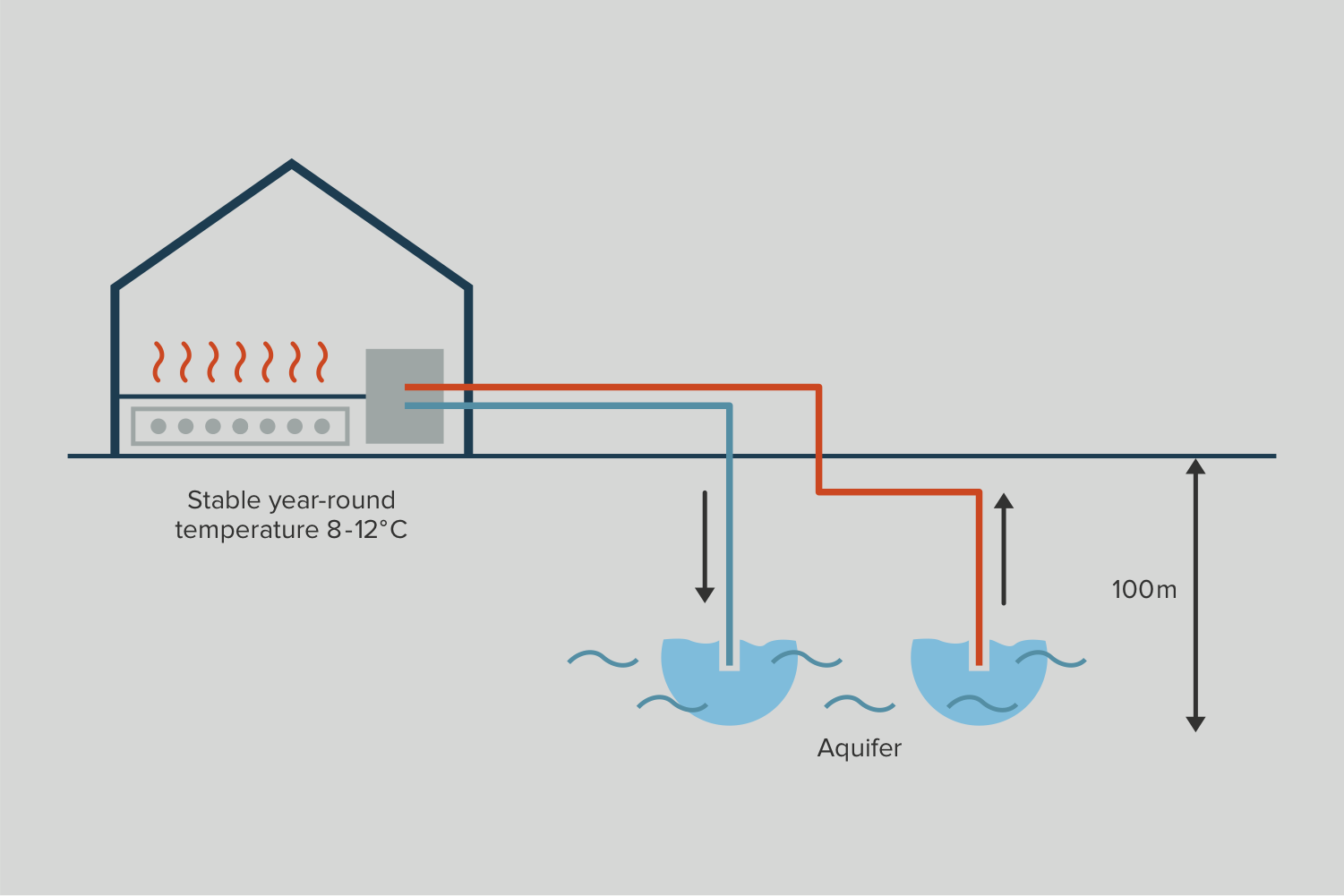
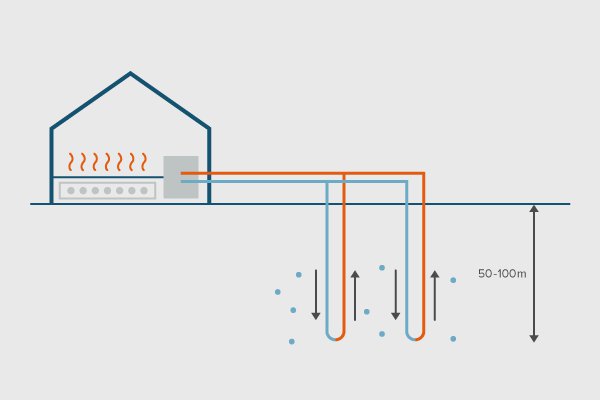
| In open loop systems the water is drawn from a reservoir of ground water (aquifer) though a bore well, is then circulated through the loop and is rejected back into the ground using injection wells. The temperature of intake water is usually stable throughout the year at around 8-12 °C. Since this loop involves continuous circulation of fresh water it is termed an open loop. The feasibility of an open loop depends on the quality of ground water as its quality potentially affects the durability of the heat exchanger and the pipes due to corrosion and fouling. It also depends on the local ground water conditions, bye-laws etc. | Closed loop systems exchange heat with the ground through the use of closed water loops. Vertical closed loops and horizontal closed loops are two popular kinds of closed loop GSHP applications. The heat exchange fluid never leaves the system and just circulating in the closed loop exchanging heat between the ground and the heat pump. In a closed loop system heat exchange fluid typically water or water with a mixture of anti-freeze or brine is circulated through pipes laid in boreholes in the ground. |
3. Space heating/cooling distribution system
Once required heating/cooling is generated by the GSHP system the space heating/cooling distribution can be done by all air systems or air water systems as described in mechanical ventilation and cooling and heating texts. Since heat pump operates at higher efficiencies while delivering lower temperature it is beneficial to integrate heat pump with radiator using an air-water distribution system. Selection of heat pump depends on the heat/cold distribution system as well as the heat exchange system whether it is an open or a closed loop system. However, most of the GSHP installations in the recent times are increasingly closed loop systems.
Area available for the installation, ground characteristics, loop technology available, cost benefit analysis are the key factors that influence the installation and performance of GSHP system.
Ground characteristics
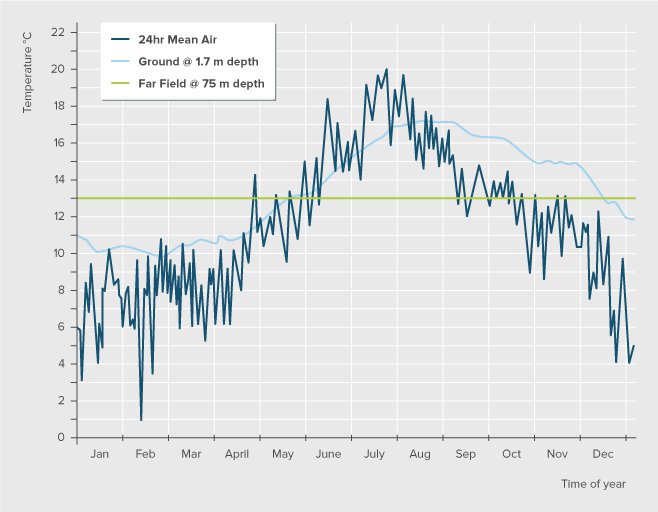
Local ground characteristics should be studied for the suitability of a ground heat exchange system. Ground temperature profile should be drawn at various depths of the soil in comparison to the mean air temperature to study the suitability of a horizontal loop or vertical loop. The type of soil and bedrock composition also plays a major role in determining the feasibility of vertical or horizontal loop systems. E.g., tight clay and sand soils suit better than soils with embedded rocks or cracked rock with gaps. In addition, the ground temperature also impacts the performance. For example in the UK at a depth of about 1.5 m the time-lag is approximately one month. Below 10 m the ground temperature remains effectively constant at approximately the annual average air temperature; between 10°C and 14°C in the UK depending on local geology and soil conditions. Figure 3, below, shows the annual variation in ground temperatures at a depth of 1.7 m compared to the daily average air temperature measured at a site in Falmouth. It also shows the ground temperature at a depth of 75 m (BSRIA).
Ground source heat exchange loop
Ground source heat exchange loop is the significant aspect of a GSHP system. The heat is exchanged between the heat pump and the ground through this loop. This happens by two methods; open loop and closed loop. Typically water is circulated through this loop using a pump that acts as a medium of heat exchange.
Sizing of a GSHP involved both the estimation of cooling and heating loads on the system and the design of the ground heat exchange system. The sizing of the ground heat exchange system is significant part of the design, as it has to be optimized to suit the heat pump operation and load. Under sizing the piping could result in the heat pump not operating at the intended efficiency while oversizing could potentially increase the capital costs. Ideally a GSHP would work best if it were designed to provide both heating in winters and cooling in summers. Though thumb rule calculations gives an initial estimate is would be best to get the systems sized and designed by an accredited professional.
Loop layout and material
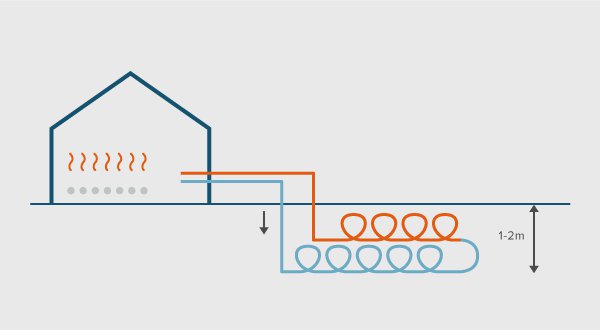
Horizontal loops are usually installed at a depth of approximately 1-2m. A minimum spacing of 3 m between the trenches is kept inorder to avoid any cross heat exchange between the pipes. Vertical boreholes should be at least 3 m and preferably 5 m apart (BSRIA). U-Shaped, high-density polyethylene pipes with a typical inside diameter of 30 mm are inserted into each bore-hole at a depth of 1-2 m below the ground surface. The boreholes are filled with grout (Harvey, 2006).
Circulating fluid and loop pump
Circulating loop typically contains upto 20% propylene gylcol solution and the composition and concentration of the fluid depends on the ground temperature to avoid freezing of the fluid. It should be kept in mind that fluid viscocity has impact on the pumping energy required and therefore should be optimized.
A typical GSHP piping arrangemnets and pumps can be seen in the table below.
| Nominal Heat Pump Capacity (kW) | 7 | 10.5 | 14 | 17.5 | 21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Required water flow Rate in m3/hr | 1.14-1.36 | 1.6-2 | 2.27-2.73 | 2.73-3.41 | 3.41-4.09 |
| Coil Type | # | # | # | # | # |
| Slinky (10 Pitch) | 3-4 | 4-6 | 6-9 | 8-10 | 8-10 |
| 6-Pipe | 3-4 | 4-6 | 6-9 | 8-10 | 8-10 |
| 4-Pipe | 2-3 | 4-6 | 5-8 | 6-9 | 6-10 |
| 2-Pipe | 2-4 | 3-5 | 4-6 | 5-8 | 6-10 |
| Vert. – 1.9 cm (3/4”) PE | 2-3 | 3-5 | 4-6 | 5-8 | 6-10 |
| Vert. – 2.5 cm (1”) PE | 2-3 | 2-4 | 3-5 | 4-6 | 4-6 |
| Vert. – 3.1 cm (1-1/4”) PE | 1-2 | 1-2 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-4 |
| Bore length | Ø | Ø | Ø | Ø | Ø |
| 30 m | 3.1 cm (1-1/4”) | 3.1 cm (1-1/4”) | 3.1 cm (1-1/4”) | 3.8 cm (1-1/2”) | 3.8 cm (1-1/2”) |
| 30-60 m | 3.1 cm (1-1/4”) | 3.1 cm (1-1/4”) | 3.8 cm (1-1/2”) | 3.8 cm (1-1/2”) | 3.8-5 cm (1-1/2”-2”) |
| Number and Size Of Pumps Required | 0.8 kW | 0.86 kW | 0.86-1.5 kW | 1.5 kW | 1.5 kW |
Heat pumps operate most efficient when producing low output temperatures, from 35-50 °C. In cold cliamtes this output temperature range most suit an air water distribution system that consits of radiator or underfloor heating rather than a forced air convective air conditioning. This makes GSHP suitable for new constructions with high insulation rather than old leaky buildings. In addition, retrofitting buildings to change the whole heating/cooling distribution system would not necessarily always be cost effective (Carbon Trust).
GSHP heat pumps are considered efficient compared to various other fuel heat sources. The efficiency can be broken down into two fold. Firstly heat pumps are inherently efficient compared to other forms of heating machines and secondly ground heat exchange makes them all the more efficient. The following table gives an estimate of the individual efficiencies of various heating and cooling systems.
| System | Primary energy efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
| Oil fired boiler | 60-65 |
| Gas fired boiler | 70-80 |
| Condensing gas boiler | 90 |
| Electrical heating | 35 |
| ASHP (heating COP/ Cooling SEER) | 250-350/10.5-15 |
| GSHP (heating COP/ Cooling SEER) | 300-500/14-30 |
A lot of the final energy consumption depends on the heating distribution system than on the primary energy efficiency of the system. In addition, fuel savings and energy savings also depend on the fuel input to the heating system. For example where gas prices are very low compared to other fuel high efficiency gas boilers are more feasible solution than a GSHP in terms of short-term returns. However, in long term GSHP offers more returns.
Factors affecting the efficiency of GSHP system
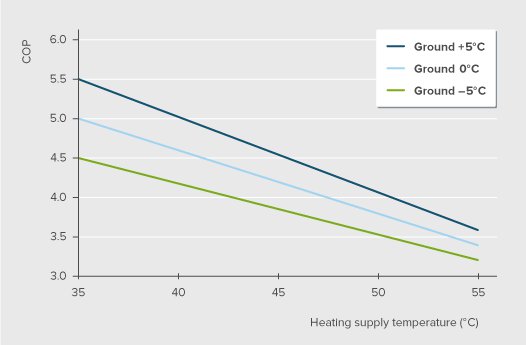
The efficiency of a GSHP system depends on the efficiency of the heat pump and the temperature gradient produced between the heating/cooling supply temperature (indoor temperature) and the temperature of the heat exchanger with which the condenser exchanges the heat. Inherent properties of heat pump such as compressor efficiency, whether it is a one state or two stage compressor etc. determine the efficiency of the heat pump. However, the COP changes with usage as the heating/cooling progresses with highest COP at the beginning of the season. Typically COP of GSHP range from 3-5 depending on various factors. In simple terms COP can be described at the ratio of useful heat produced per unit of eclectic power input. The following graph shows the COP in relation to the heating supply temperature and the difference between the stable ground temperature and the supply temperature. It can be observed from the following graphs (see figure below) that at the dT increases and the heating supply temperature decreases the COP of the GSHP system increases significantly.
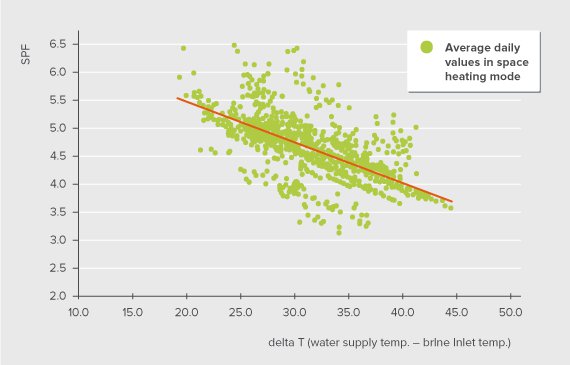
A study conducted by the Fraunhofer ISE as Seasonal Performance Factor (SPF) as indicator of the performance based of measured data of various air, water and ground source heat pumps indicates that the GSHP outperforms the other two forms of heat pump. Unlike COP, SPF takes into account energy consumed by all the components such as pumps, auxiliary heating etc. and heating produced both for space heating and domestic hot water. The data puts the average SPF of a GSHP at 3.72, of an air to water heat pump at 2.99 and water-to-water heat pump at 3.39 till the measured data was available (Miara, 2011). SPF in relation with the difference between the water supply temperature (on the distribution side) and brine inlet temperature (inlet temperature of ground heat exchanger in closed loop systems) can be seen in the figure below.
Laying of horizontal loop heat exchanger is relative easy and than the vertical loop heat exchanger. Vertical loop heat exchanger requires on site drilling of boreholes into which the heat exchange pipes are inserted. Different types of drilling methods suit different types of soil and different depths. Popular drilling methods include Rotary drilling, Auger drilling, Air core drilling, Diamond core drilling and Direct push rigs and drilling. The kind of drilling methods available limits the feasibility of Vertical loop heat exchanger.
Commissioning, installation of key components, calibration and maintenance
The following steps should be followed while installing a GSHP system
The heatpump equipment and heat exchanger should protected from external weather in a casing and preferably kept indoors.

makes energy efficiency in buildings and appliances transparent. For investors, policy-makers and actors involved in implementation and consultancy. Learn more ...
© 2024 | Built by the Wuppertal Institute for Climate, Environment and Energy | All rights reserved. | Imprint | Privacy Policy
