Shading buildings from the sun’s radiation requires the understanding of the earth’s movement around the sun, radiation from the sun and how to protect buildings from it or use it in favour of buildings de-pending on the climate. Understanding the basics of shading such as earth’s movement, sun path dia-grams, shading masks, shading devices, the calculation methodologies and tools help in the effective design of shading devices. All the aspects explained here in sequence aims only to provide the reader with a basic understanding of the subject and elaborate references are made to authoritative texts for deeper understanding on the subject.
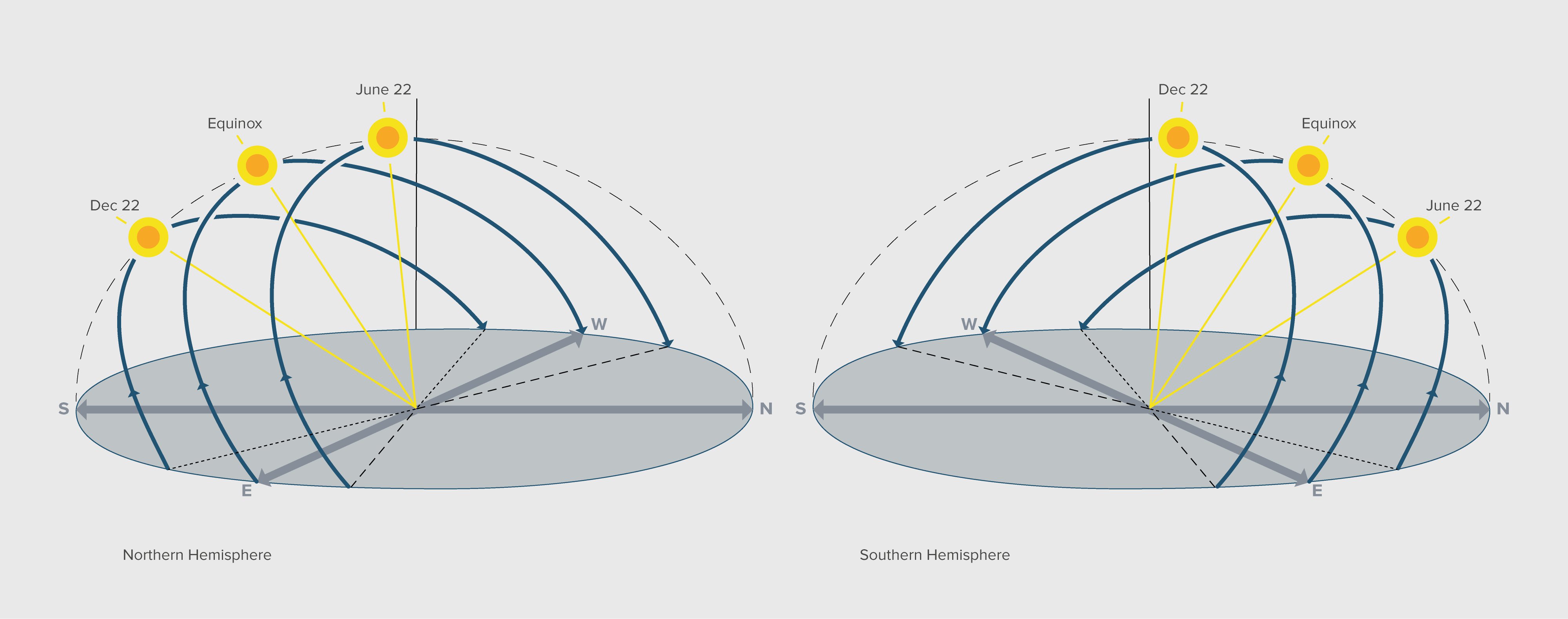
The Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit and the plane of revolutions is knows as ecliptic and also rotates around an axis called the axis of rotation. The axis of Earth’s rotation is tilted 23.45° perpendicular to the ecliptic. The angle between the plane of the equator and the ecliptic is knows as the declination angle. Conventionally, the angle of declination is considered to be a positive +23.45° on June 22, i.e., northern solstice and a negative -23.45° on December 22, i.e., southern solstice. On the equinox days, i.e., March 22 and September 21, the Earth’s equator lies in the plane of ecliptic and the angle of declination is considered to be 0°.
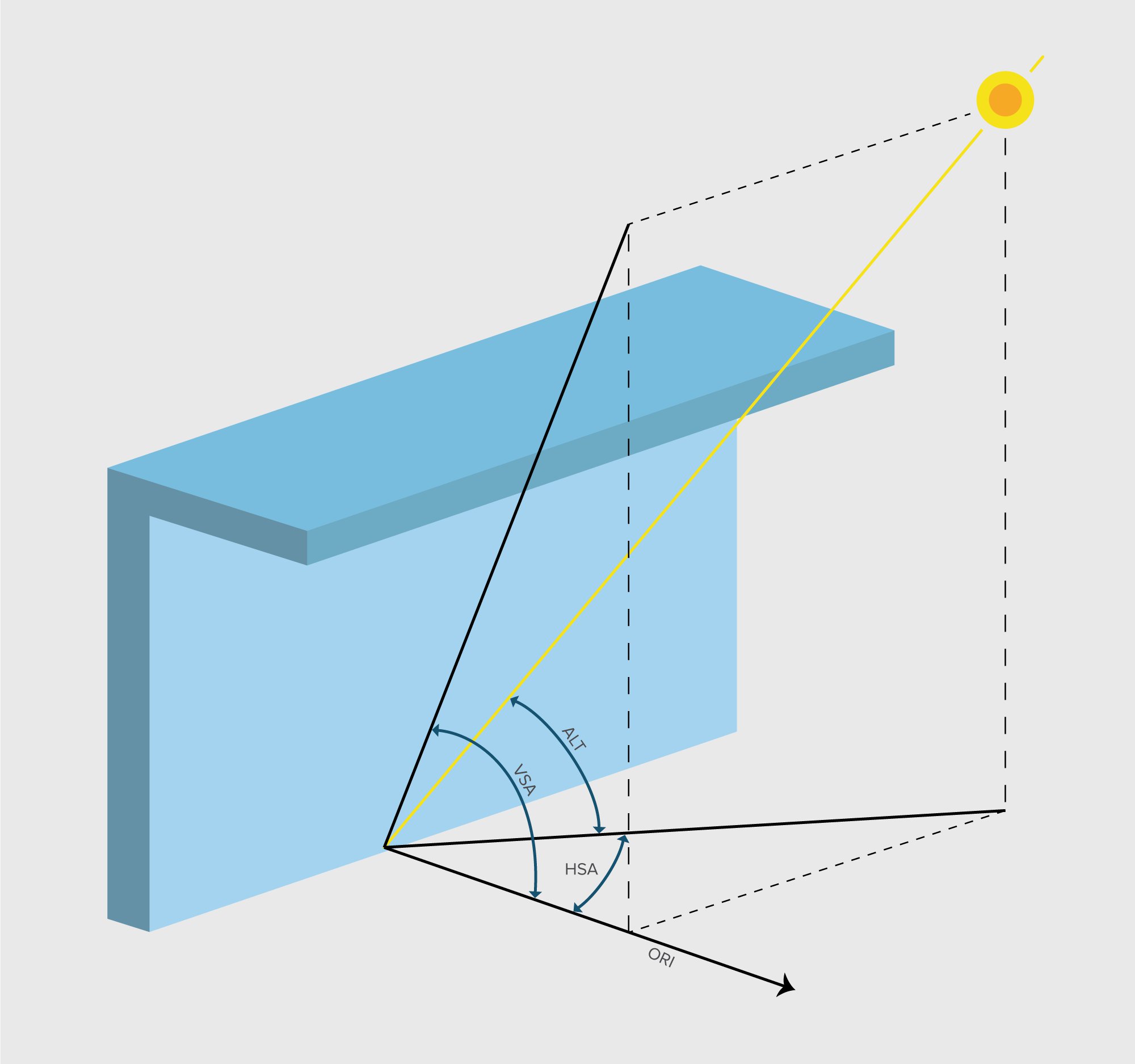
Although heliocentric view better explains the location, tilt and orientation of the earth around the sun in an elliptical orbit, for all practical purposes related to calculation of solar radiation on earth, a geocentric view is considered which deems the earth at the centre and tracks the suns movement relative to earth. The sky is considered to be a semi spherical vault and the earth’s horizon is assumed to be flat. The key terms that define the exact position of the sun relative to the earth are given below.
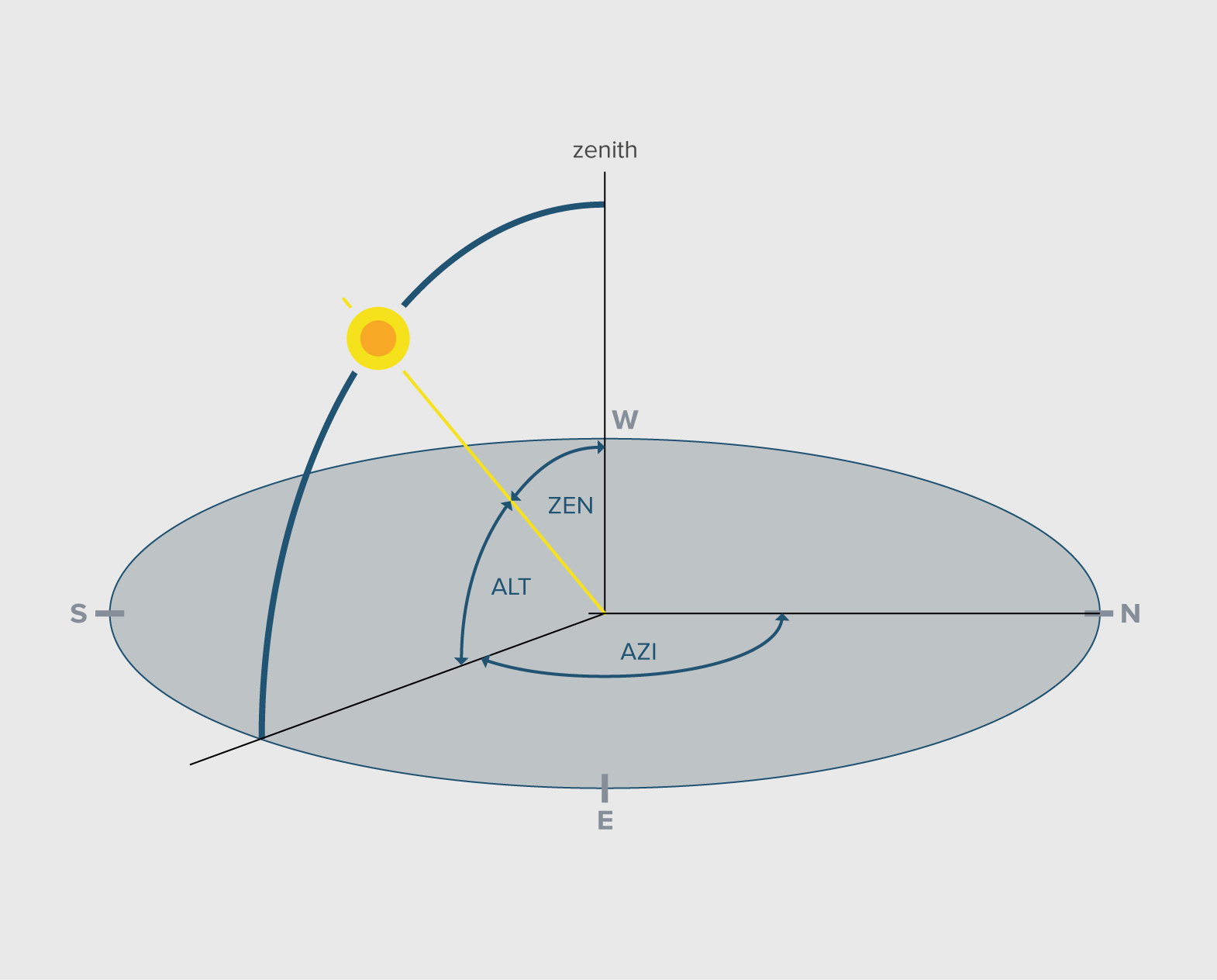
Altitude
Altitude angle (ALT) or the elevation angle is the angle between the axis of the sun pointing towards the earth’s centre and the earth’s horizon plane.
Azimuth
Azimuth angle (AZI) is the angle between the North of the earth’s horizon plane and the projection of the sun perpendicularly downwards on the earth’s horizon plane in a clockwise direction.
Zenith
Zenith angle (ZEN) is the angle between the axis of the sun pointing towards the earth’s centre (at any time) and the axis formed at the solar noon when the sun is at the peak. It is also given as 90° - Altitude an-gle.
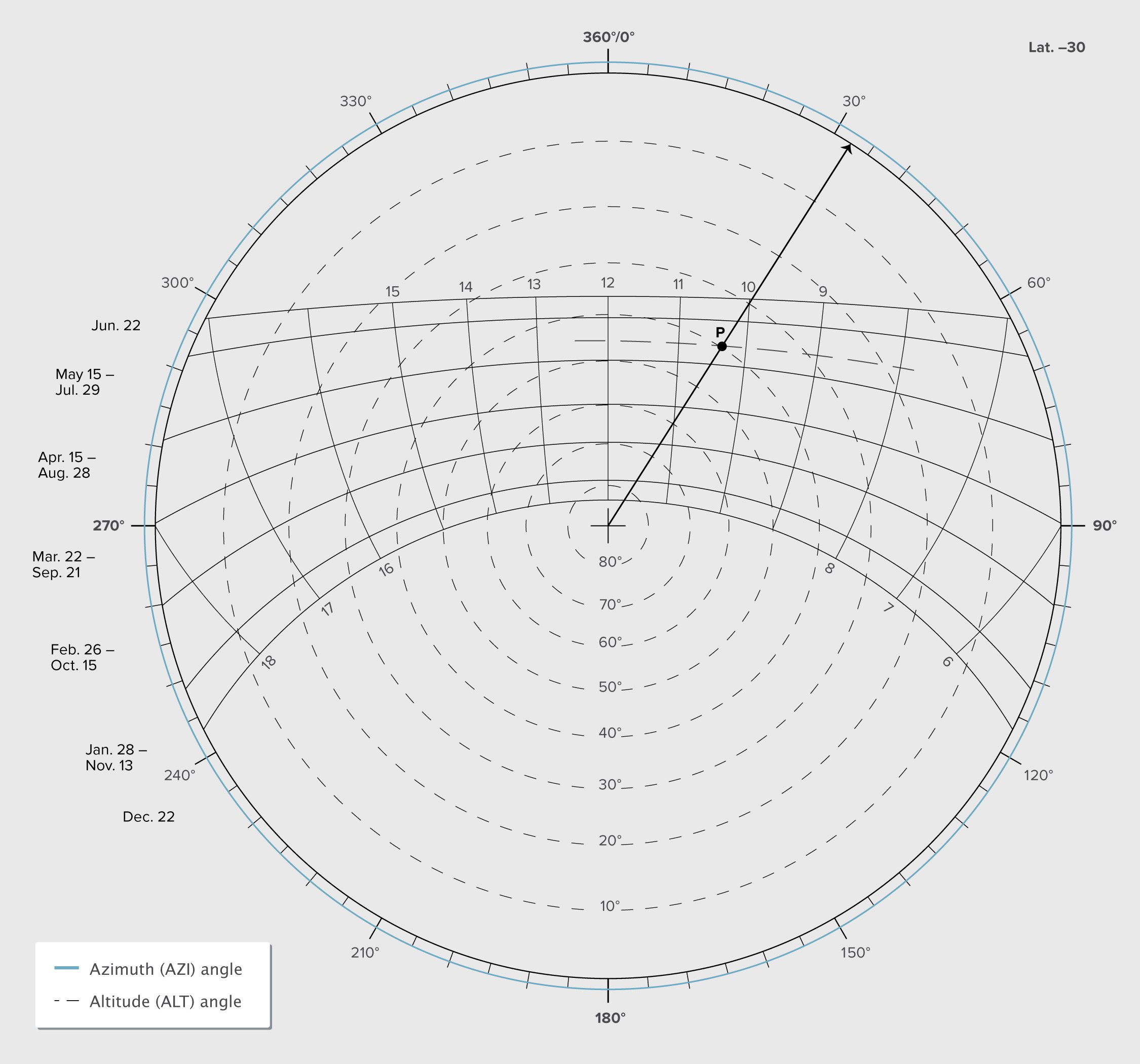
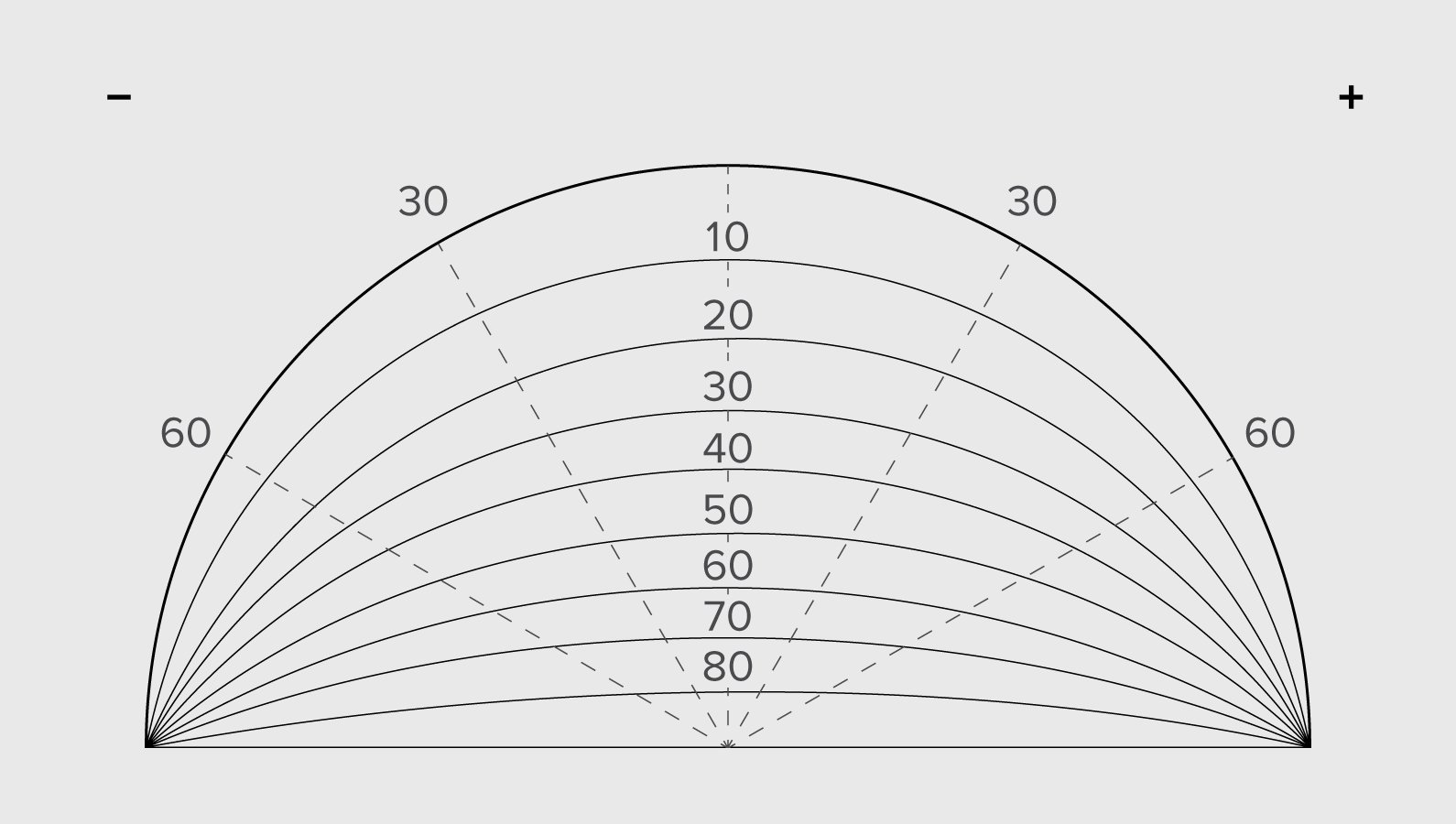
Sun-path diagrams represent the movement of the sun in a three-dimensional sky hemisphere projected on a two-dimensional surface. They typically consist of relevant details such as the Altitude, Azimuth, time and date of the year and the movement of the sun in graphical form. Polar projections and Cartesian projections are two types of common projection systems for making sun-path diagrams. Polar projections will be discussed hereafter for their simplicity of understanding and widespread usage.
Polar projections
In polar projections the horizontal earth’s plane (azimuth) is represented in a circle divided into 360° while the altitude is represented from angles 90° which is the centre of the circle to the 0° which is the external most circle representing with marking for the azimuth angles. Three forms of polar projections are used namely spherical, equidistant and stereographic projections of which stereographic projection is most widely used.
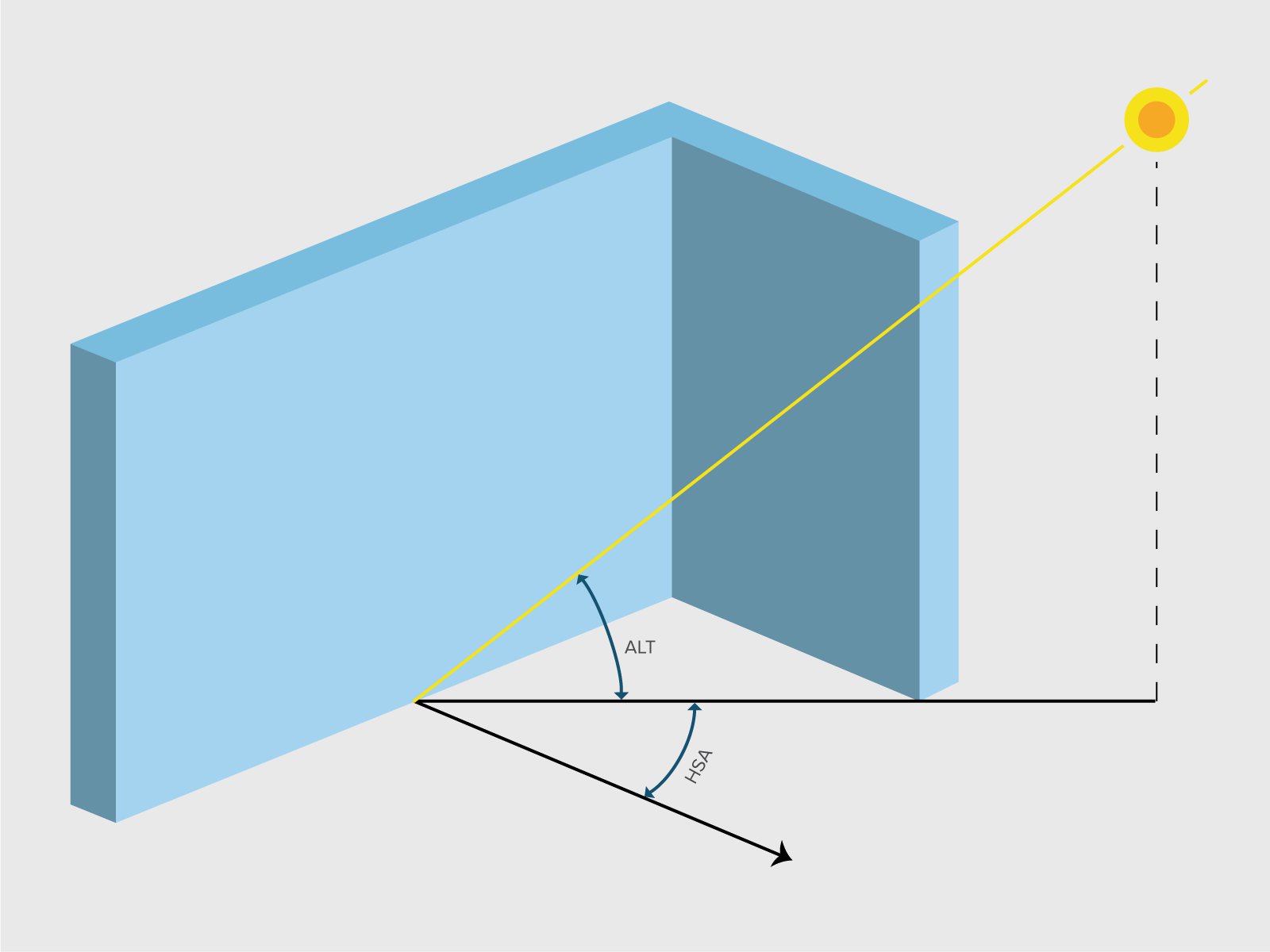
Horizontal Shadow Angle (HSA) and Vertical Shadow Angle (VSA) are key indicators in designing of shading devices and can be calculated if the solar azimuth and altitude angles are known.
Horizontal Shadow Angle
The angle between the normal to the surface of the wall or window and the azimuth angle of the sun gives the Horizontal Shadow Angle. When the surface is in shade, the HSA is typically between +/- 90° to 270° and there is no HSA. The design and performance of a vertical shading device is determined by the HSA.
HSA = AZI (azimuth of the sun) – ORI (Azimuth/Orientation of the facade)
Vertical shadow angle
Vertical Shadow Angle is slightly complex to calculate than the HSA. When the façade directly faces the sun, i.e., AZI = ORI (HSA = 0°) the VSA is the same as the solar altitude angle (VSA = ALT). At all other angles of when HSA ≠0°.The design and performance of a horizontal shading deceive depends on the VSA. The VSA is given by the equation:
VSA = arctan(tan(ALT)/cos(HSA))
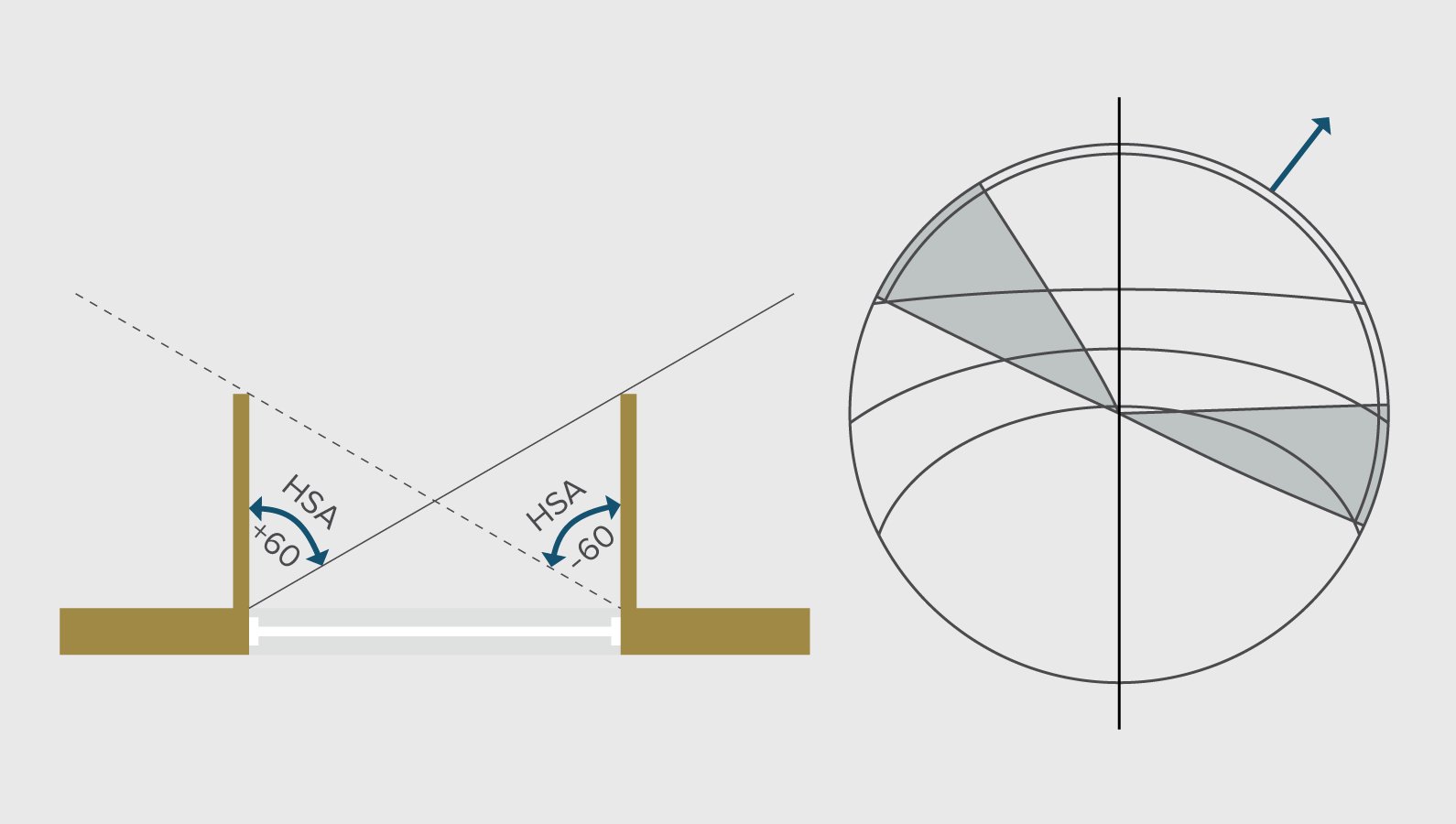
Shadow angle protractor
A shadow angle protractor is a semi circle with HSA and VSA lines marked on it. HSA lines are projected radially outward from +90° to -90° and VSA lines are arcural lines whose centre overlaps with the altitude circles in a stereographic diagram.
Horizontal shadow angle
Consider the following example where a window is seen in a sectional plan. For the window to be shaded from edge to edge a vertical shading device with a shadow angle of 60° is required. The projection of shadow angle line also gives the dimensions of the shading device required. The shading mask for the shading device marked on the shadow protractor looks like the figure on right. The shaded part in the protractor represents a shadow mask that
indicates that the surface remains shaded. The shading mask thus
produced is laid over a sun-path diagram and is oriented to represent
the azimuth of the surface. Then shaded area in the shadow mask shows
which period of the year, i.e., month, date and time a particular
surface (window/wall) remains shaded.
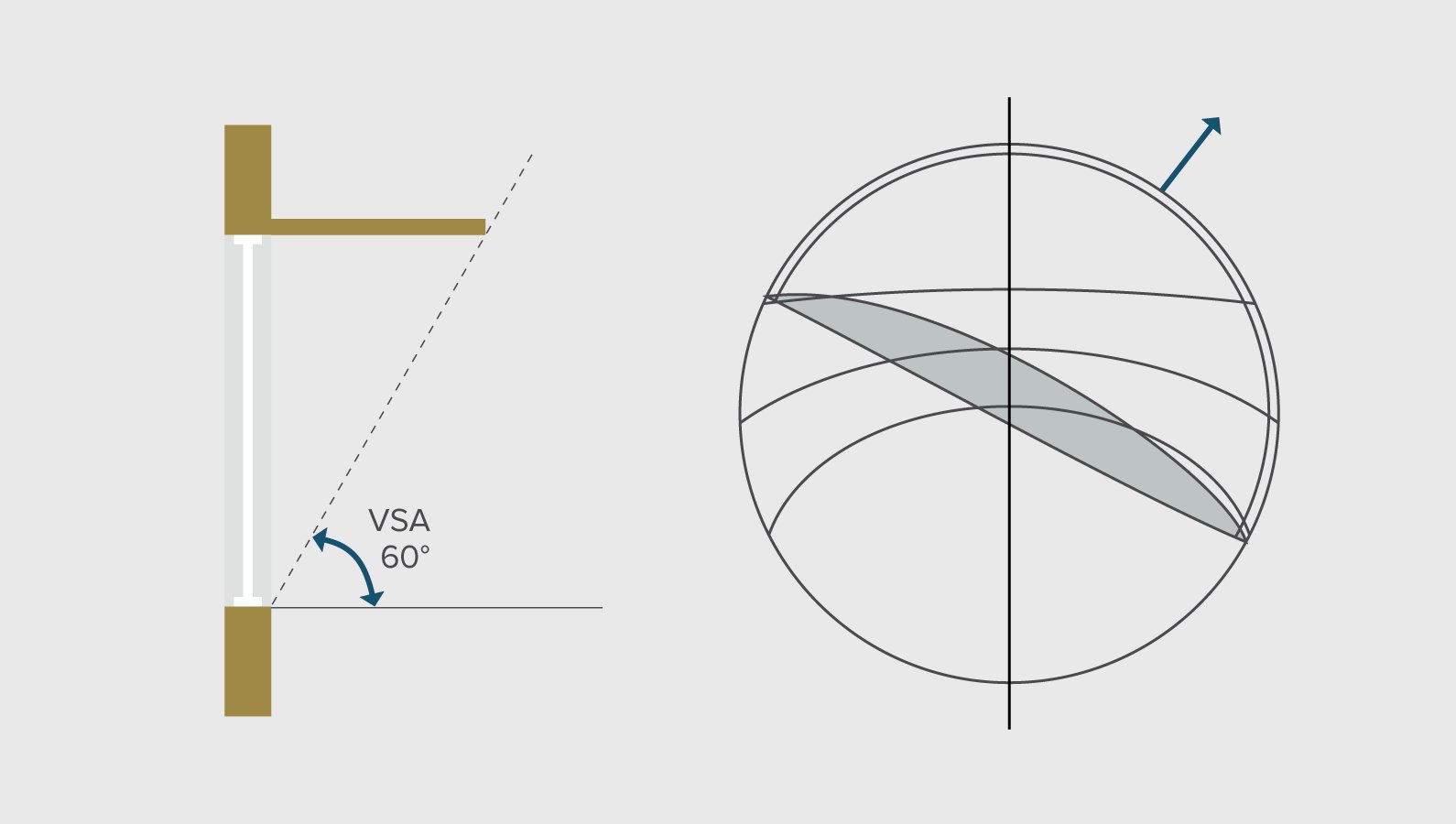
Vertical shadow angle
Consider the following example where a window is seen in a sectional elevation. For the window to be shaded from top to bottom a horizontal shading device with a shadow angle of 60° is required. The projection of shadow angle line also gives the dimensions of the shading device required. The shading mask for the shading device looks marked on the shadow protractor looks like the figure on right. The shaded part in the protractor represents a shadow mask that
indicates that the surface remains shaded. The shading mask thus
produced is laid over a sun-path diagram and is oriented to represent
the azimuth of the surface. Then shaded area in the shadow mask shows
which period of the year, i.e., month, date and time a particular
surface (window/wall) remains shaded.
An overshadow diagram for a single point gives the information of the portion of sky that is obstructed because of the surrounding buildings and vegetation. The sun is also obstructed when it is directly behind these blocks. An overshadow diagram can be constructed for any location manually by projecting the surfaces onto an imaginary hemisphere around the point and then representing the same on a two-dimensional surface, typically a stereographic diagram. Other way of constructing is to use a 180° fish eye lens and tracing the outer lines of all the surroundings blocks. An overshadow mask construct-ed either way is laid over a sun-path diagram and period of obstructions for sun can be exactly traced.
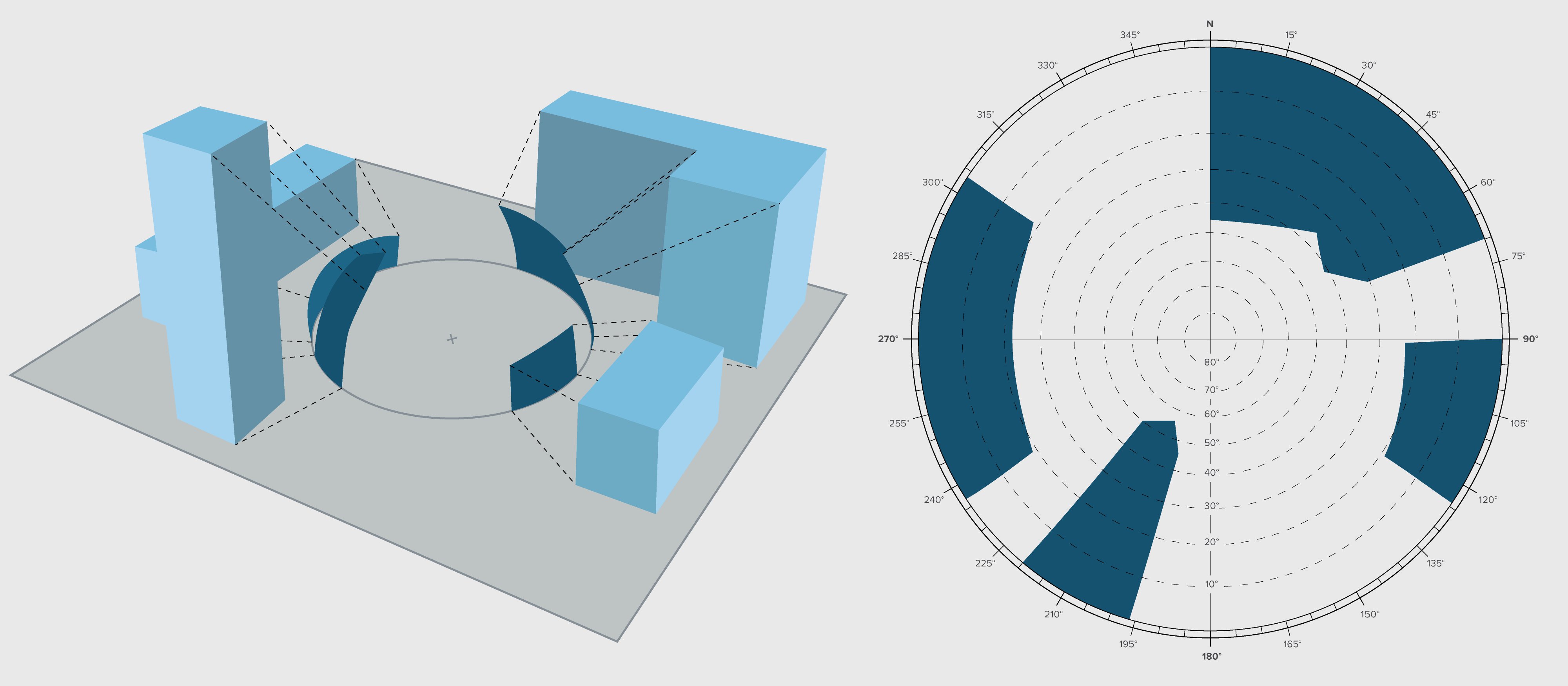
The process of shading design involves the following steps:
When is shading needed? - Determination of shading period
It is important to decide when shading is needed for a particular surface. Typically in hotter climates shading is always required while in cooler climate shading is required only in winters and sun penetration is required in winters for passive solar heating. There are several ways to determine when shading is required. One simple and popular way of doing is to determine “overheating period”. Overheating period is when the monthly mean temperature is higher than the lower thermal comfort limit. This can be determined by plotting annual mean monthly temperature and thermal comfort. This is a simplistic way to determine shading period for buildings with less or negligible internal loads.
Alternately, computer programmes such as SHADE and CHAYYA describes a more complex approaches for determining the shading period through an approach called “Balance Point Method” (CED, 2011; Sami & Olgyay, 2009). This is useful for buildings with considerable internal loads, glazing area and seldom desire sun for passive heating of the building.
Using shading protractor and sun-path to generate shading mask and determine HSA and VSA
Once the period, during which the shading requirement is determined, a shading mask can be generated using the combination of a shadow protractor, sun path diagram for that particular latitude. A shadow protractor should superimposed over the sun path diagram by orienting the protractor to align with the azimuth angle of the surface for which shading is designed. By marking the points on the protractor HSA and VSA are determined which in turn gives the dimensions of the shading device using trigonometric calculations. o
Shading coefficient/SHGC
The glazing type of the windows is also important in terms of solar heat gains through the glass. Important characteristic of glazing that determines its effectiveness is a factor called “shading coefficient (SC)”. Shading coefficient is the value of the amount of direct solar radiation passing through a particular glazing divided by the direct solar radiation passing through a clear float glass. SC for a glazing is between 0 to 1. However, SC is giving way to a new factor which is referred to as “Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)”. SHGC, unlike SC, takes in to account the amount of solar radiation passing though an entire window system including its frame. SHGC is roughly given as 0.87 multiplied by SC. Lower SHGC value represents a better performing glazing system.
Tint
Tint can be used to effectively reduce the amount of solar insolation entering the building. Tint should be used carefully as shading as it has the effect that the glazed surface can reach quite temperatures due to the thermally absorbed heat. This heat then can radiate as long wave radiation into the interior. In temperate and cold climates such glazing also has the negative effect that in winter the solar insolation entering the building is greatly reduced. Thus despite a good solar heat gain coefficient of the glazing, direct shading of the windows and openings of a building must be thus sought first. At high angles of incidence, of about 80° the glazing can achieve up to 50% more reflection than a vertical window. Glazing can be inclined to reduce solar heat gain through reflection, the affectivity is however, dependant on the latitude of the building.
Shading elements can be classified into purpose-built devices (fixed and adjustable) and non-purpose built shading elements such as trees and plants, as well as aspects of site and location and shading from other buildings (please see the document “Site and Microclimate” for more information). Orientation of the openings, combined with their size and tilt can modulate the solar gains passing through them. This must be taken into account when designing shading devices. Shading elements can also be architectural features of the building itself such as balconies, vestibules, integrated façade design or planters etc. Purpose built shading devices are either fixed or adjustable. These can be further divided into:
Horizontal Shading
Horizontal shading is most effective for equator-facing facades and windows where there is a high altitude of the sun especially in the tropics. Care must however be taken to prevent a build up of hot air under horizontal shading especially with windows and air intakes in this plane. Long verandas and roof overhangs also work satisfactorily in hot climates and in many cases are accomplished with canvas tents or pergolas. Roof overhangs can be integrated into the planning are among the least expensive shading devices especially in single story buildings. In open strategy buildings that rely on natural ventilation horizontal window shading can also be integrated into the window shutters in form of louvers.
In cold and temperate climates openings, horizontal shading, can accept solar heat gains when desirable, for example, during winter and can easily be shaded during summer, owing to the high position of the sun in the sky. Pergolas have the advantage that when covered with deciduous plants they can shade in summer and allow solar insolation to the façade in winter.
Vertical Shading
Vertical shading is most effective on east and west façades. The shading of west and east windows presents more difficulties because of the low position of the sun in the sky during morning and afternoon hours and, additionally west-orientated openings are associated with conditions of high solar radiation and ambient temperature during summer. Thus, it is advisable that windows in this orientation should be minimised or replaced with other design solutions, such as south- or north-facing openings in these facades. Vertical shading elements and trees on east and west facades work best to protect the walls and windows from the low angle morning and evening sun. Vertical shading is most effective with the sun to the side of the window.
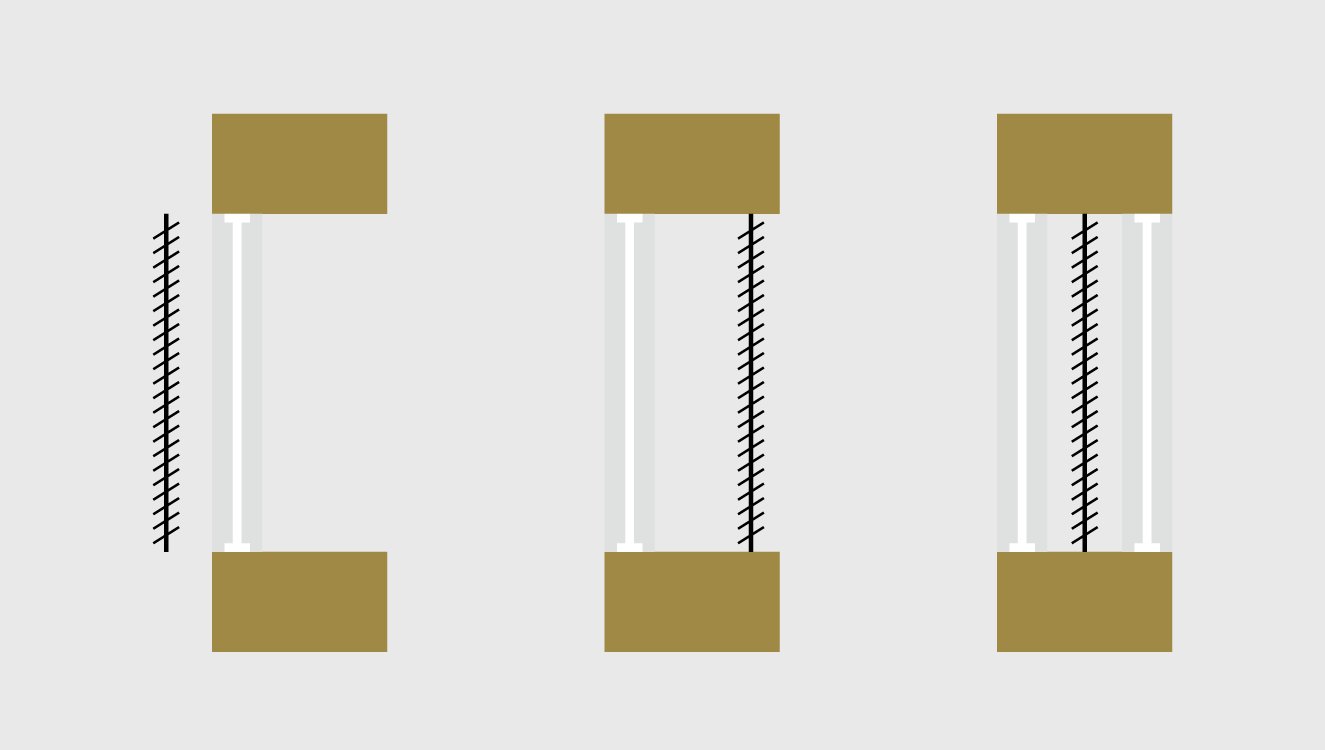
Combined Horizontal and Vertical Shading or “Eggcrate shading”
For
façades which neither horizontal nor vertical shading is optimal a
combination of both through latticing or “eggcrates” can be used to
achieve optimum shading. This combination excludes more insolation than a
single strategy alone and should thus be only used where no internal
heating from solar radiation is needed.
Adjustable shading devices can respond better to the dynamic nature of the sun’s movement, allow better control of the diffuse radiation and glare while enabling day lighting and in most cases, cause less or negligible sun obstruction during winter. Adjustable shading devices can be more effective for optimized energy use as they can be adjusted to the conditions. This is especially relevant in temperate and cold climates where shading in late hot summers and early autumns as well as the benefits of solar gain in late spring might still be needed. Fixed shading which can only be sized for a certain period does not account for this.
Shading devices for fenestrations can be either placed externally or internally. However, there are differences between internal and external shading devices in terms of their effectiveness in reducing solar gain and in their usage. External shading elements are generally about 35% more effective than internal ones (Olgyay, 1963).
Internal Shading
Internal shading devices can only intercept that solar radiation that has already passed through the glass. This means it can only eliminate that portion of solar energy that can be reflected back through the glass to the outside. The rest is absorbed and reradiated into the room through convection. The effectiveness of internal shades is thus mainly determined by their reflectivity. Internal shading although protecting the deeper interior of a building have the negative effect that are behind the glazing and the greater part of any heat blocked or absorbed by the internal shading is within the thermal envelope.
External shading
External shading devices on the other hand,
lose the convected and reradiated portion of the solar energy to the
outdoor air. This energy will thus not heat the interior further.
Internal shading devices may also conflict with day lighting and
ventilation requirements, because in most cases they block the openings.
Application of awnings can effectively reduce summer heat gains by up
to 65% on equator facing facades and by up to 80% on east and west
facades (Harvey, 2006). Louvre on an East or West facing façade can
reduce solar heat gain.
Vegetation can be used as shading elements to great effect. Depending on the type of vegetation and the climate they can provide generous shading at the right seasons. In Hot climates shading should be for example evergreen to provide shading throughout the air with care being taken in hot and humid climates not to block cooling breezes. In Temperate and cool climates these should be deciduous to allow the winter sun to reach the building façade. Trees and plants also have an especially beneficial effect on the thermal performance of buildings and on the physical environment in general. They reduce air borne sounds; their viscous leaves catch dust and filter the air.
In winter evergreen windbreaks can reduce the heat loss from buildings and discourage drifting snow. In summer the surface of grass and leaves absorb radiation, and their evaporation processes cool the air. Green Façades can also provided shading on dark façades to help reduce solar insolation. Pergolas covered with vines can also be used for shading. One drawback of vegetative shading is the time taken for the shading to grow and in hot and humid climates they can reduce ventilation in open and hybrid buildings. Another drawback of vegetative shading is the height of the vegetation and thus it can only be used on relatively low buildings.
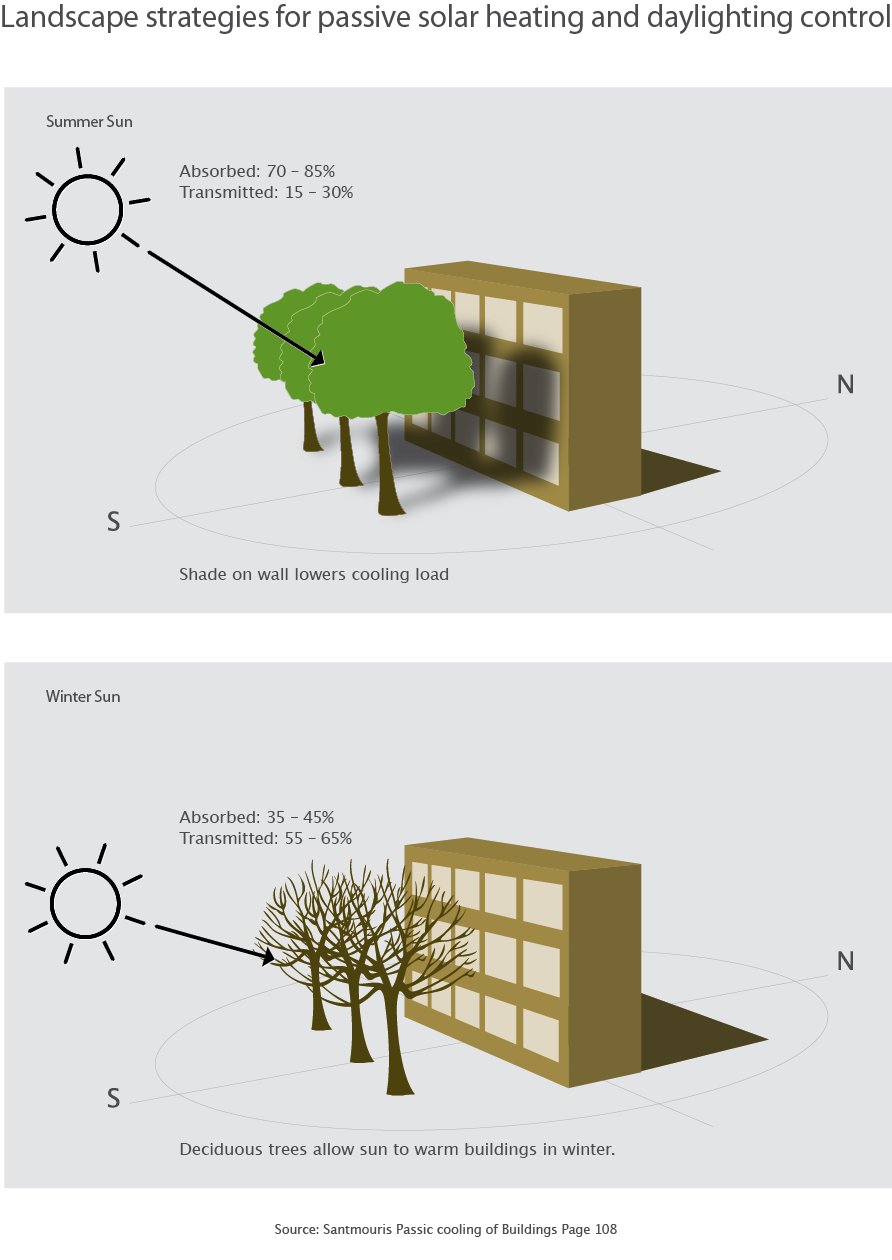
The Shading through surroundings other buildings can also play a part in the solar gain. Poorly planned buildings in temperate and cold climates might be totally shaded in winter reducing their useful solar gain. In Hot climates shading through landscape can be beneficial. In Hot-Arid climates where cross ventilation through breezes is not of ultimate importance shading can also be beneficial through the buildings themselves. This is achieved through a high building density where the buildings are close and shade each other.
Verandas
Verandas are for example and ideal means of providing shade to the main building as well as offering an open living space, that acts as a buffer between outside and inside and which breezes can naturally cool.
Roof Shading
Through the use of large overhangs especially on low-rise buildings roofs can be used to shade the façades of buildings.
Fly-Roof Shading
The
internal heat gain at the ceiling level can be reduced through the
shading of the upper ceiling through lightweight roofs. The space
between the roof surfaces also allows for ventilation and aids the
removal of heat build-up.
One of the major problems with shading elements is that the amount of light penetration deep in to the interiors is reduced. To improve this any of the above shading elements can be modified to give a more even distribution of lighting across the room.
Light Shelf
One such solution is that of the light shelf which diffuses the light as well as reflects it into the interior. These are horizontal shading devices which are placed ideally slightly below the top of but not directly attached the window. The upper surface that should be bright white reflects light into the interior and at the same time shades the large part of the window below. Other common light guiding elements are panels with holographic optical elements (HOE), light-guiding glass, revolving lamellas, prisms and Venetian blinds. These elements are however not effective for low-angle sunrays.
| Orientation | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Pole facing | Shading is not required beyond the tropics; between the equator and the tropics horizontal fixed shading is recommended |
| Equator facing | Fixed horizontal shading |
| East and west | Fixed vertical shading |
| NE & NW & SE & SW | Adjustable or fixed egg crate shading and vegetation |

makes energy efficiency in buildings and appliances transparent. For investors, policy-makers and actors involved in implementation and consultancy. Learn more ...
© 2024 | Built by the Wuppertal Institute for Climate, Environment and Energy | All rights reserved. | Imprint | Privacy Policy
